
Heat of Fusion Definition, Equation & Examples Video & Lesson Transcript
I explain the definition of Latent Heat and how it's used in the equation Q = mL, how to identify the latent heat of fusion, vaporization, and sublimation, a.
Phase Change Requires Heat FD2021 Fundamentals of Fire and Combustion on Guides
latent heat, energy absorbed or released by a substance during a change in its physical state (phase) that occurs without changing its temperature.

Latent Heat Of Fusion Definition Class 9 cloudshareinfo
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process—usually a first-order phase transition, like melting or condensation.. Latent heat can be understood as hidden energy which is supplied or extracted to change the state of a substance without changing its temperature or.
Latent Heat Water My XXX Hot Girl
construct a phase diagram by specifying the phase(s) observed at particular P,T combinations: t. the latent heat involves a change in internal energy, plus work in expanding the volume. Examples of latent heats: material fusion, L f (J / kg) vaporization, L v (J / kg) water 33.5 x 104 22.6 x 105 ethyl alcohol 10.8 x 104 8.55 x 105

draw labelled diagram of the experimental set up to the latent heat of fusion of ice Brainly.in
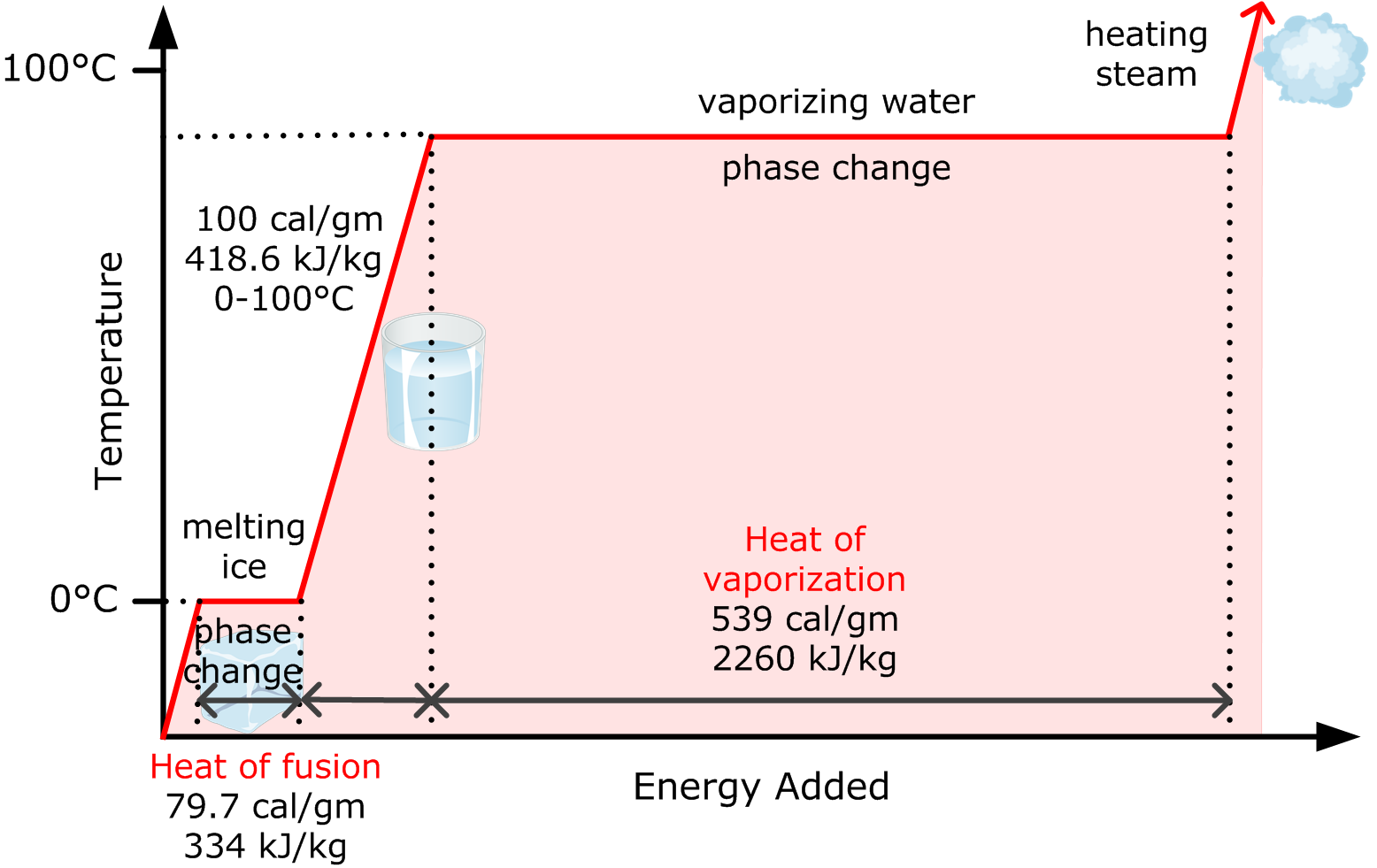
Step 3: Calculate the latent heat of fusion. Calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of ice to water using the equation ΔE = LΔm. ΔE = Energy supplied by the heater = 10, 000 J; L = Specific latent heat of fusion; Δm = mass of ice; Rearrange the equation; So, = 340136 J kg-1 = 340 000 J

Four Differencebetween latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporization Brainly.in
What the heck is dry ice and why is it so spooky? Learn this and more when we investigate phase changes and phase diagrams!Watch the whole General Chemistry.

unit08 latent heat of fusion YouTube
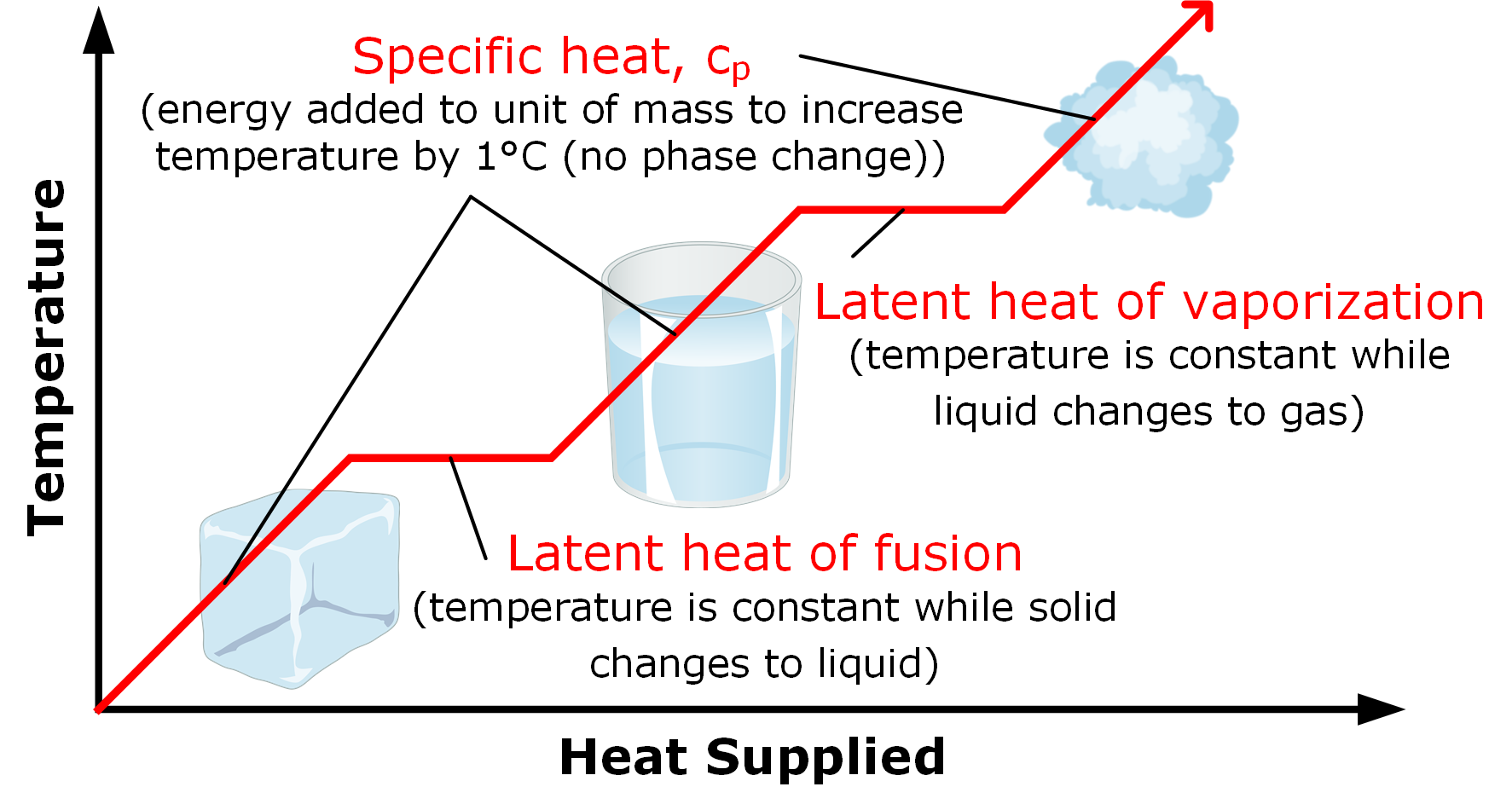
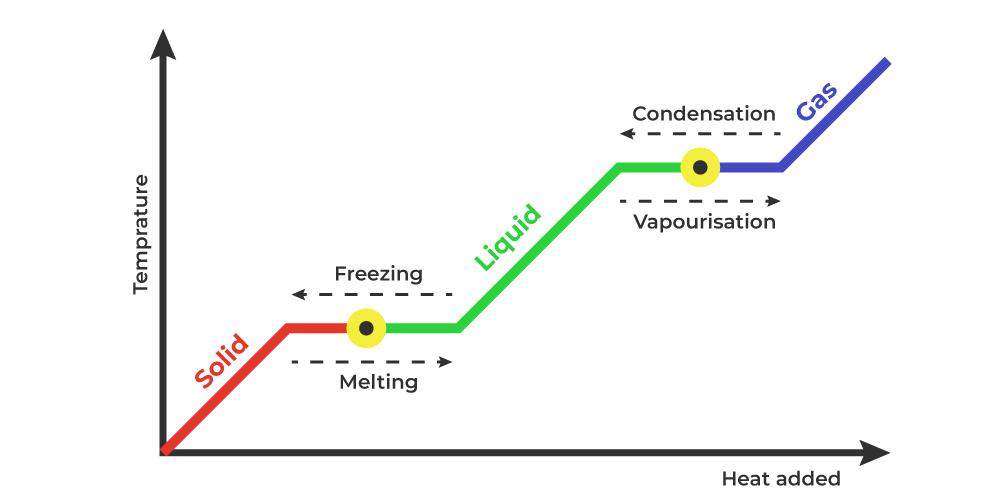
Phase changes Transitions between solid, liquid, and gaseous phases typically involve large amounts of energy compared to the specific heat.If heat were added at a constant rate to a mass of ice to take it through its phase changes to liquid water and then to steam, the energies required to accomplish the phase changes (called the latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporization) would.

Latent heat YouTube
Latent heat of evaporation (at 100°C): 40.657 kJ/mol = 2256 kJ/kg = 970 Btu (IT)/lb C): 999.975 kg/m = 1.9403 slug/ft = 8.34519 lb /gal (US) Melting temperature (at 101.325 kPa): 0 °C = 32°F pH (at 25°C): 6.9976
Latent Heat of Fusion Definition, Formula, Examples & FAQs
Overview. The 'enthalpy' of fusion is a latent heat, because, while melting, the heat energy needed to change the substance from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure is latent heat of fusion, as the temperature remains constant during the process.The latent heat of fusion is the enthalpy change of any amount of substance when it melts. When the heat of fusion is referenced to a unit of mass.

Specific Latent Heat Of Evaporation Formula Specific Heat Capacity And Latent Heat Enthalpy
The latent heat of fusion refers to the phase change between states of solid and liquid. Here, heat actually refers to the transfer of heat energy between the objects. Thus, the latent heat of fusion encompasses the process of adding heat to melt some solid. The formula for Latent heat of fusion:

Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases Teachoo Science
The phase diagram for carbon dioxide shows the phase behavior with changes in temperature and pressure. The curve between the critical point and the triple point shows the carbon dioxide boiling point with changes in pressure.
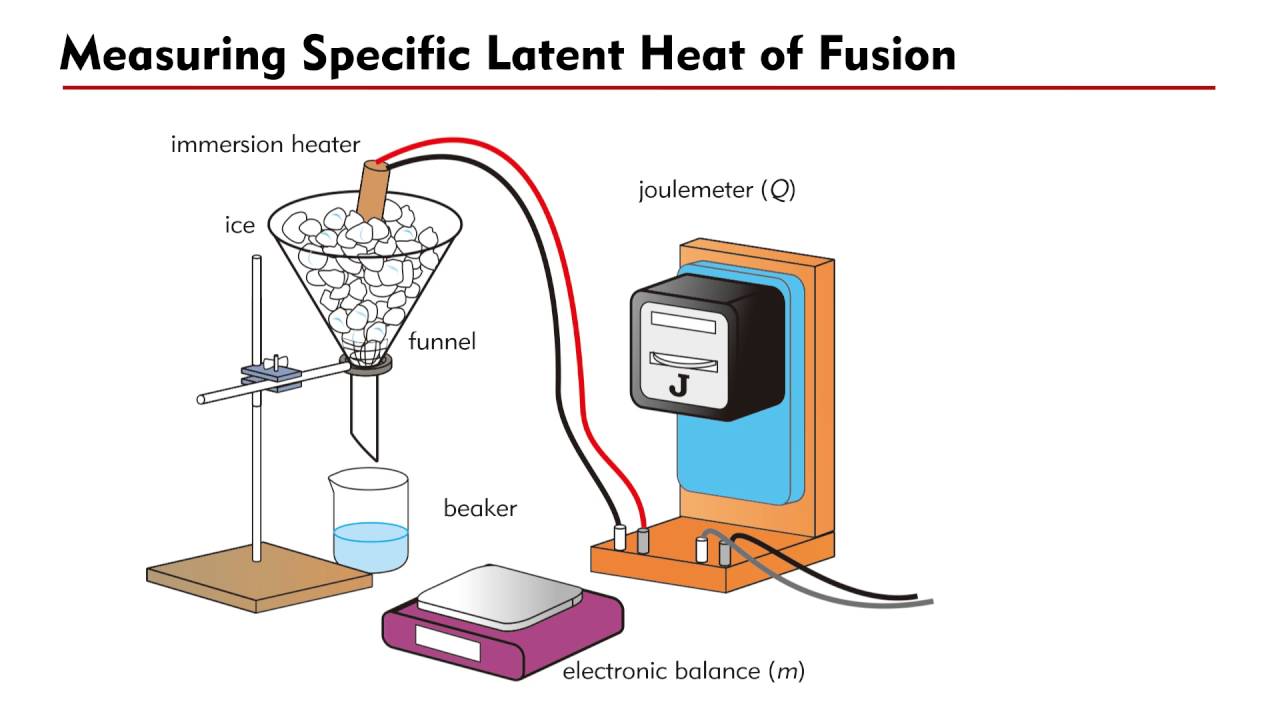
Measuring the specific latent heat of fusion of Ice YouTube
Latent heat is measured in units of J/kg. Both L f and L v depend on the substance, particularly on the strength of its molecular forces as noted earlier. L f and L v are collectively called latent heat coefficients.They are latent, or hidden, because in phase changes, energy enters or leaves a system without causing a temperature change in the system; so, in effect, the energy is hidden.

Solved Latent Heat of Fusion Lab Instructions In this lab
Because this energy enters or leaves a system during a phase change without causing a temperature change in the system, it is known as latent heat (latent means hidden ). The three phases of matter that you frequently encounter are solid, liquid and gas (see Figure 11.8 ).
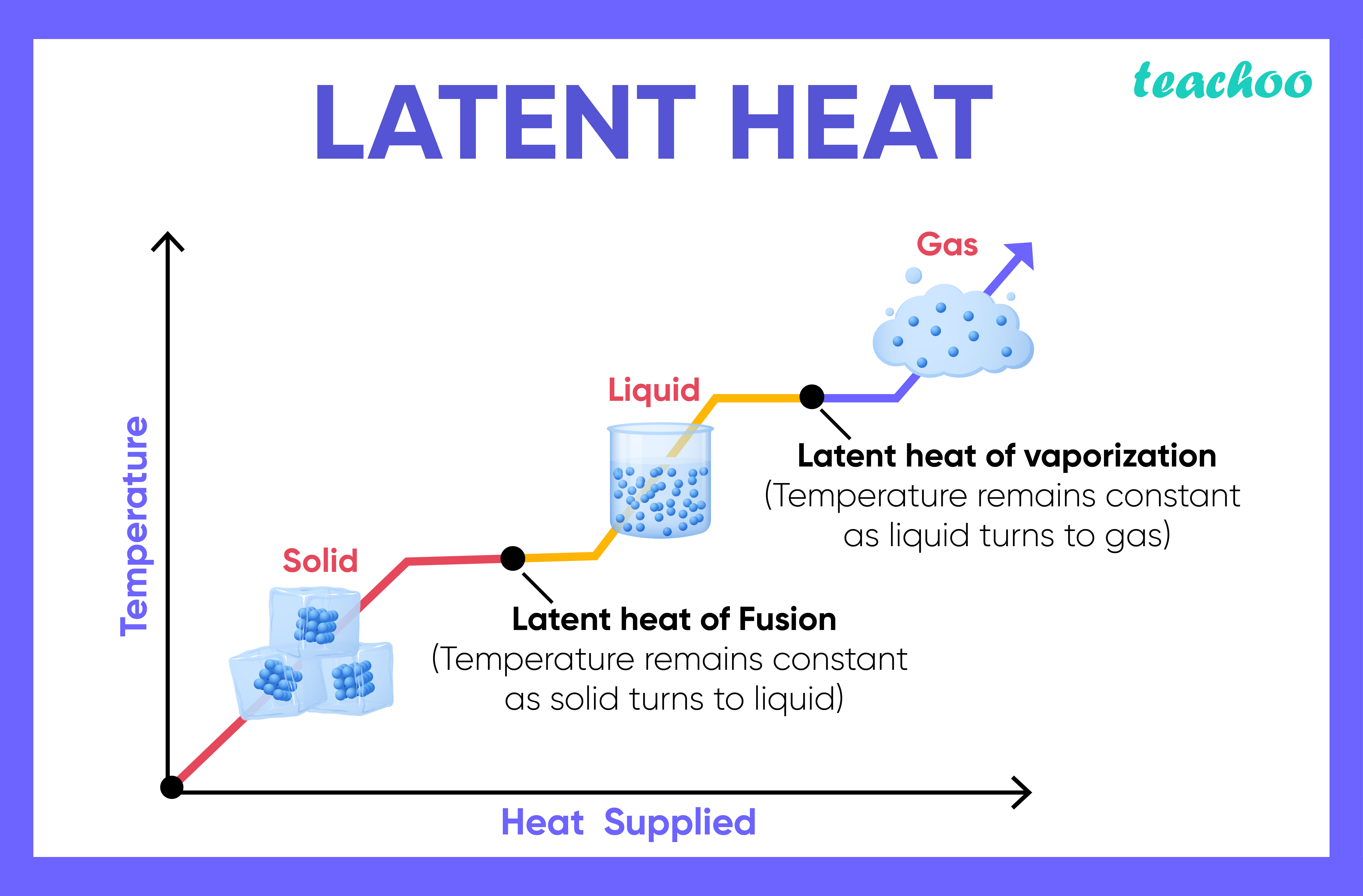
For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the
Latent heat is defined as the heat or energy that is absorbed or released during a phase change of a substance. It could either be from a gas to a liquid or liquid to a solid and vice versa. Latent heat is related to a heat property called enthalpy. Download Complete Chapter Notes of Thermodynamics Download Now

PPT Change of State PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6691426
The latent heat of fusion of the eutectic, Δ fus H E, is estimated from the total change in entropy on fusion, Δ fus S E. To evaluate the thermodynamic models, we compared the values estimated by these models with experimental values reported in the literature, and values obtained here for two eutectic mixtures of fatty acids: a eutectic.

Latent heat of fusion for common wrought alloy families. Download Scientific Diagram
Using the equation for a change in temperature and the value for water from Table 14.2, we find that Q = mLf =(1.0kg)(334kJ/kg)= 334 kJ Q = mL f = ( 1. 0 kg) ( 334 kJ/kg) = 334 kJ is the energy to melt a kilogram of ice. This is a lot of energy as it represents the same amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of liquid water.