
what are the parts in a cross section of a leaf and what are their functions? Brainly.in
(Cross Section in Above Right Photo) Color is produced by the balance of pigments in the leaf tissue and also by the distribution of pigments in the plastids as well as the air spaces inside of the leaf that scatter the light penetrating into the leaf.
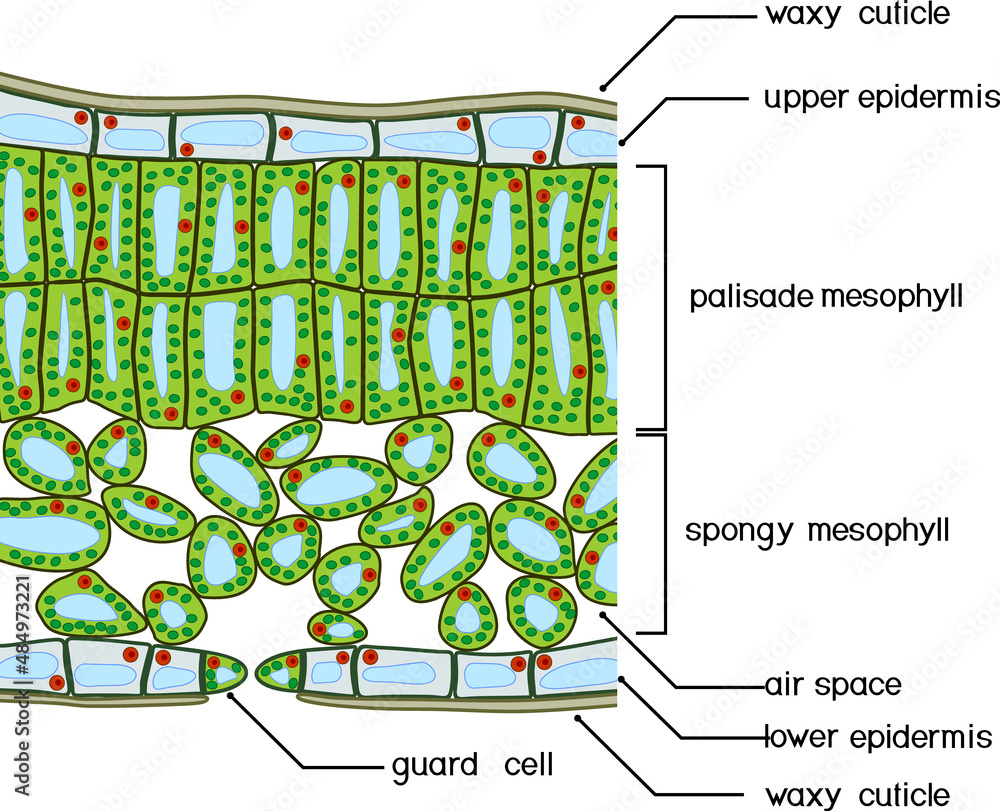
Plant Leaf Cross Section
PHOTOSYNTHESIS [INTRO] Parts of a Leaf CrossSection of leaf.mov CROSS SECTION OF A LEAF Cuticle: A waxy layer that prevent water loss by evaporation. The cuticle is transparent and very thin to allow maximum light penetration. Upper Epidermis: A protective layer of cells that produces the cuticle.
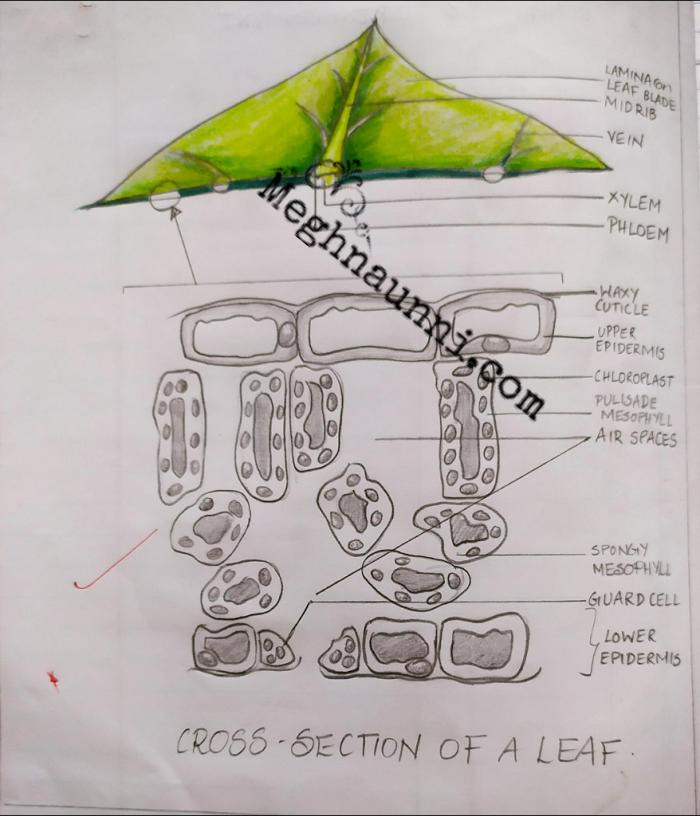
Cross Section of a Leaf Biology Diagram
Views of Cross Section of Syringa Leaf Paradermal-Section : In this plane of section we clearly see each tissue layer in face view. First, identify the upper epidermal layer. The upper epidermis can be differentiated from the lower because it has fewer stomata.
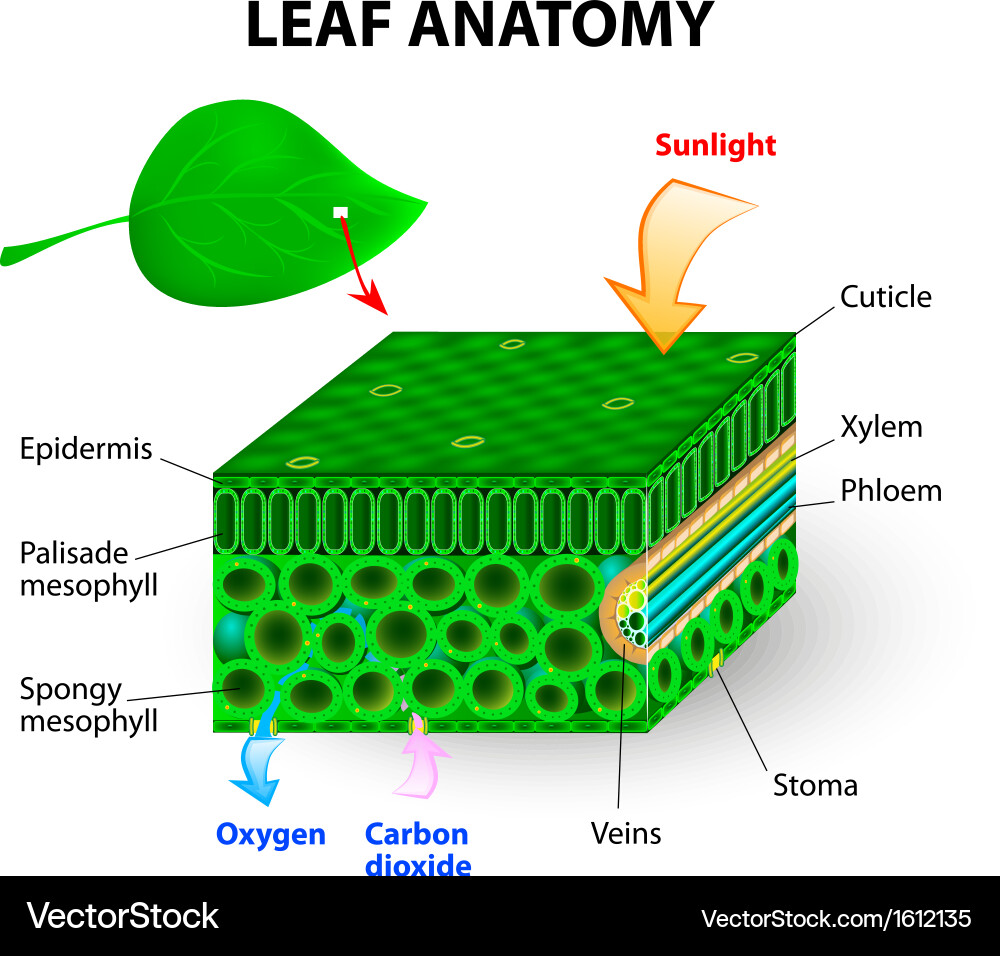
Leaf anatomy Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock
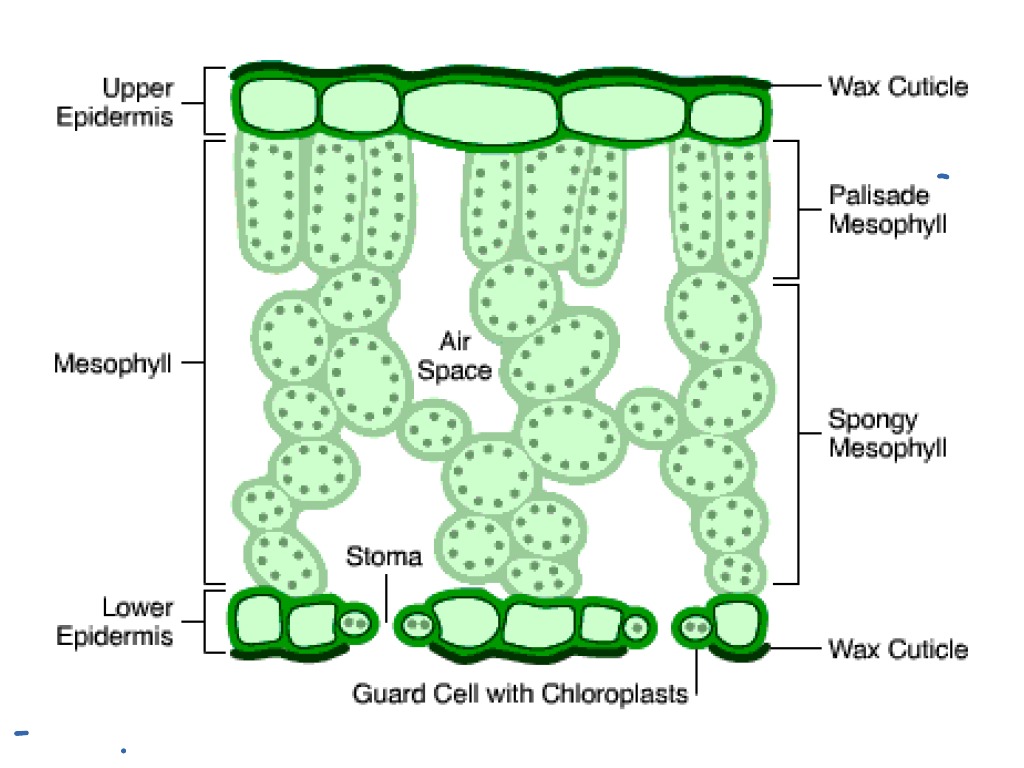
FIGURE 3. A cross section of a leaf. are responsible for most of the photosynthesis in the leaf and are called the palisade mesophyll. Located under the palisade mesophyll are loosely packed cells called the spongy mesophyll. The spongy mesophyll forms air spaces that hold raw materials to be used and products of
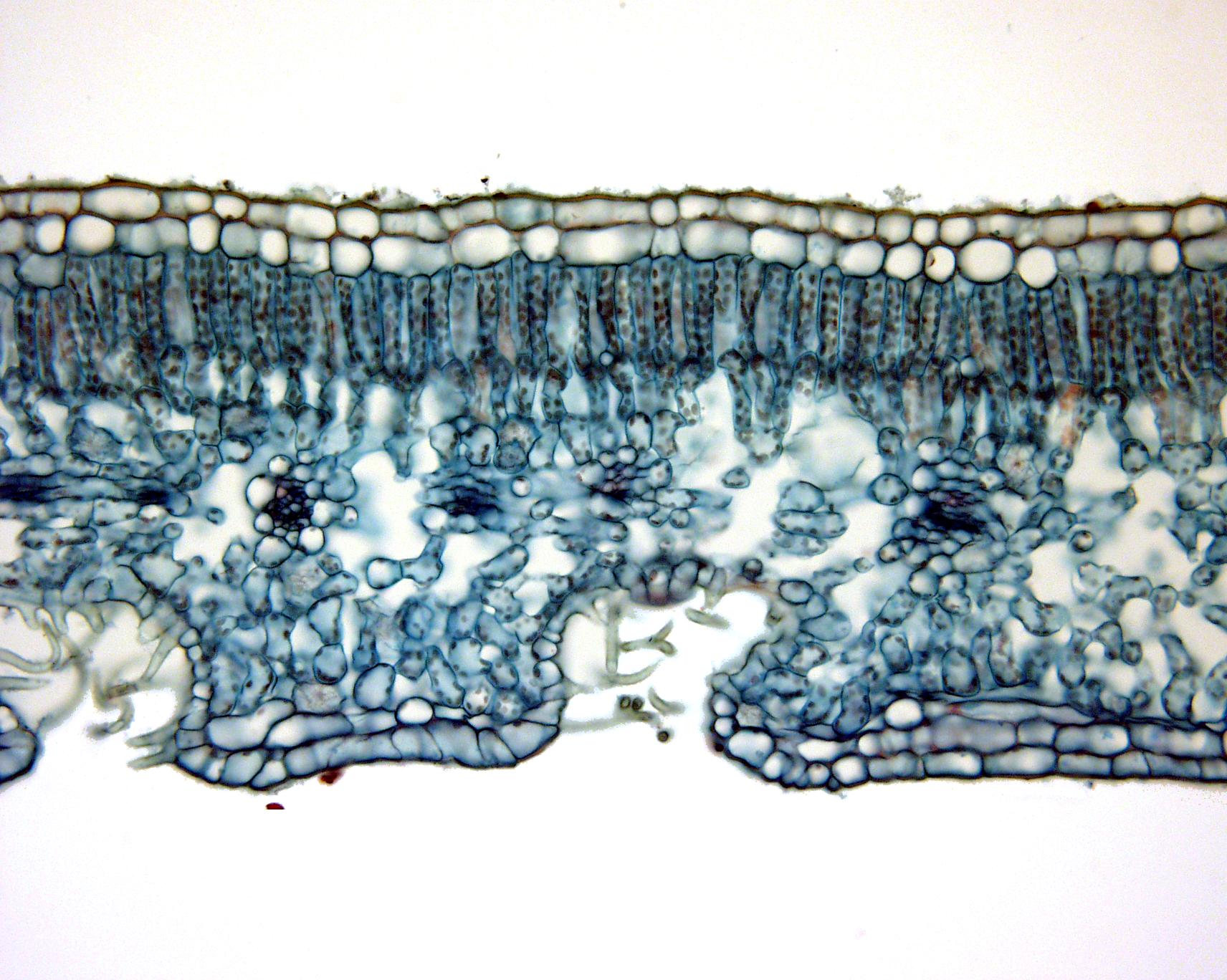
Cross section of a leaf blade of Nerium oleander a xeromorphic plant UWDC UWMadison
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): A cross section of a corn (Zea mays) leaf. See the caption in Fig. 13.2.3 for a detailed description of the features present. Photo by Maria Morrow, CC BY-NC. Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): A cross section of a section of a corn leaf, labeled. The upper epidermis is composed of parenchyma cells that appear empty.

Leaf Structure photo Botany, Teaching biology, Biology
1 General characteristics 2 Morphology Toggle Morphology subsection 2.1 Basic leaf types 2.2 Arrangement on the stem 2.3 Divisions of the blade 2.4 Characteristics of the petiole 2.5 Veins 2.6 Morphology changes within a single plant 3 Anatomy Toggle Anatomy subsection 3.1 Medium-scale features 3.2 Small-scale features 3.3 Major leaf tissues
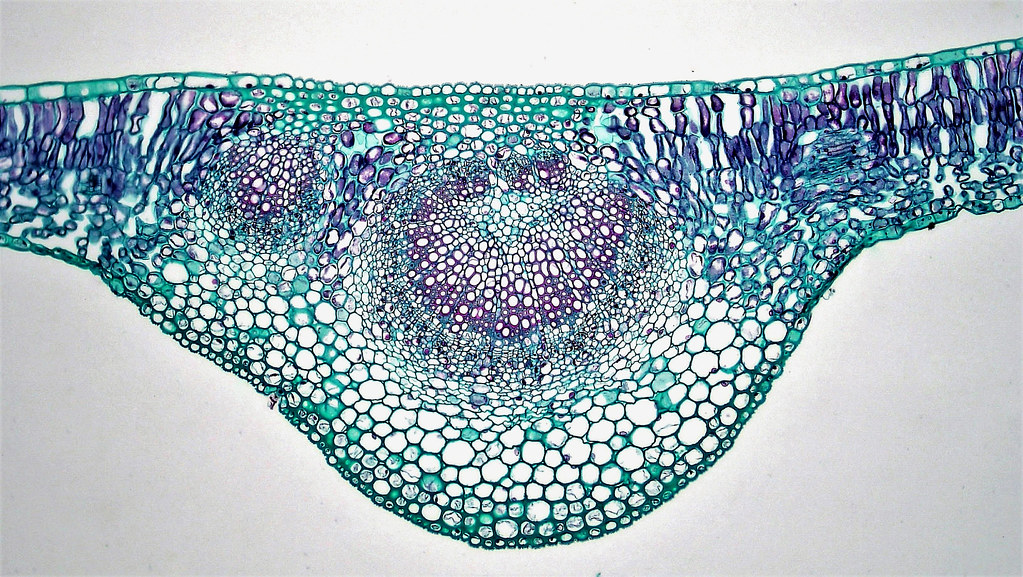
Dicotyledonous Leaf Cross Section designsbylima
Figure 9.3. 2: Cross section of a hydrophytic leaf. Observe a prepared slide of a hydrophyte, such as Nymphaea, commonly called a water lily. Note the thin epidermal layer and the absence of stomata in the lower epidermis. In the spongy mesophyll, there are large pockets where air can be trapped.
Cross Section Of A Leaf Diagram Labeled Wiringopedia
A cross-section through a leaf Features of leaves and their functions The role of stomata The control gas exchange in the leaf. Each stoma can be open or closed, depending on how its guard.

Leaf anatomical features (a) leaf cross section with dense crystal... Download Scientific Diagram
A cross section of a leaf shows that it is a complex organ built of several different kinds of specialized tissues. The tissues, in turn, are built of specialized cells, and the cells, of organelles. [Figure1] Epidermis covers the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf.
Plants Leaves
New version of this video: https://youtu.be/_y-HCi7mJjMThis is a description of a leaf cross section at the cellular level. Leaves contain a number of differ.

Cross Section Of A Dicot Leaf olddominiondesigningdivas
The air space found between the spongy parenchyma cells allows gaseous exchange between the leaf and the outside atmosphere through the stomata. In aquatic plants, the intercellular spaces in the spongy parenchyma help the leaf float. Both layers of the mesophyll contain many chloroplasts. Figure 30.10. 1: Mesophyll: (a) (top) The central.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/leaf_crossection-57bf24a83df78cc16e1f29fd.jpg)
Plant Leaves and Leaf Anatomy
What are the primary components observed in a leaf cross section? What is the difference between palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyll? How are stomata observed under the microscope? What is the role of the epidermal layer in a leaf? Why do leaves have air spaces in the spongy mesophyll?
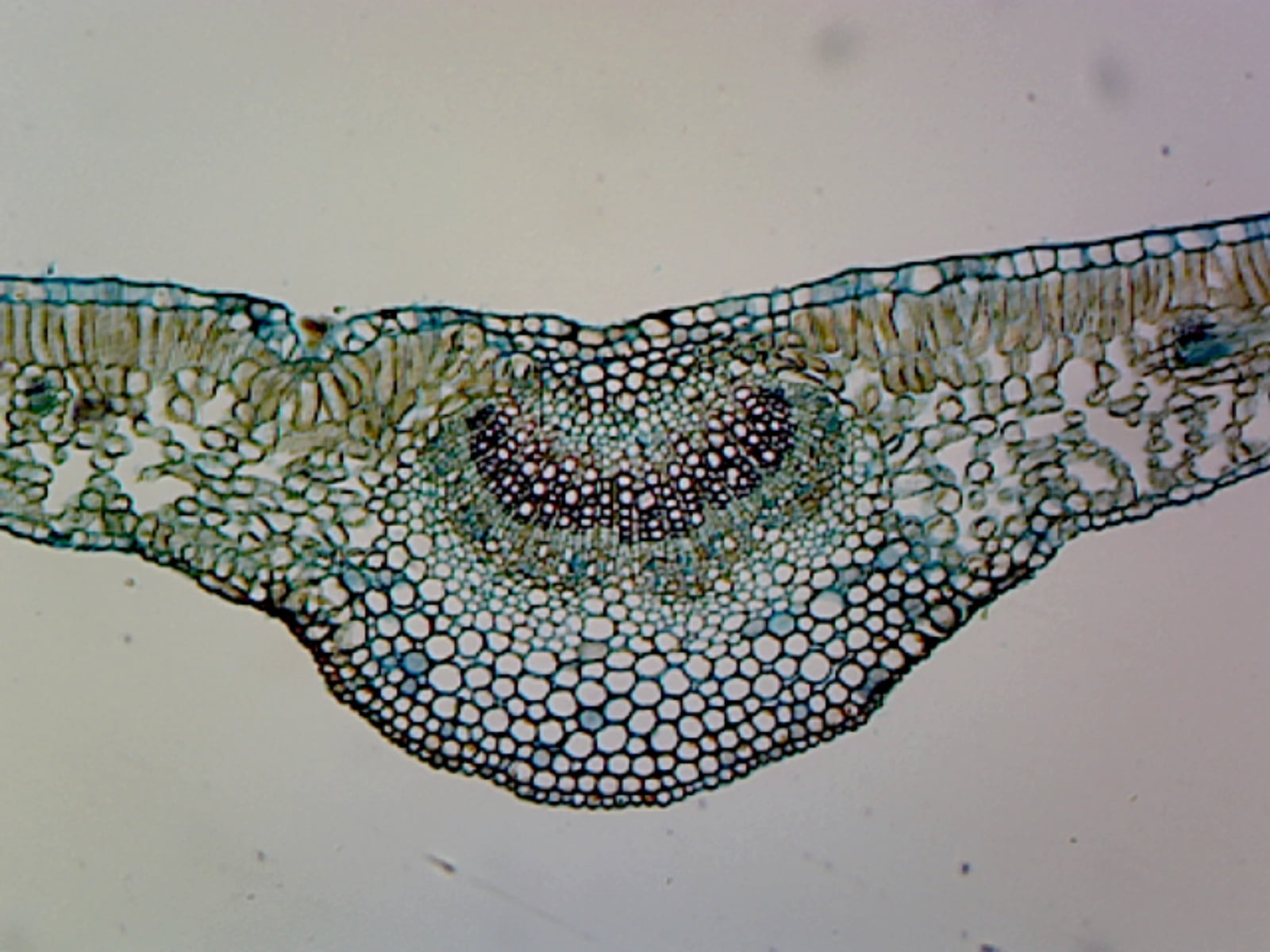
GSC International PS0079 Ligustrum Leaf; Showing Typical Mesophytic Dicot Leaf; Cross Section
Leaf Structures Table. Diagram showing the cross-section of a leaf. The specialised cells in leaves have adaptive features which allow them to carry out a particular function in the plant; Adaptations of Plant Leaves for Photosynthesis Table. You've read 0 of your 0 free revision notes

Draw a diagram of a cross section of a leaf and label it? Brainly.in
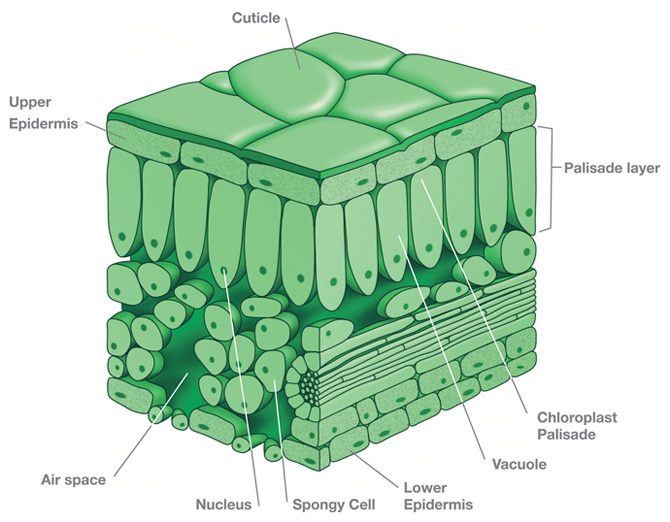
Leaf. The main function of the leaf is photosynthesis. Therefore, it contains many chloroplasts and is thin to facilitate gas and water transport. View the leaf model and the leaf cross section slide. Make sure you can identify the following components: Epidermis (upper and lower) Cuticle ; Spongy Mesophyll ; Palisade Mesophyll ; Xylem; Phloem

Draw and label the parts of a T.S. of a dicot leaf. Brainly.in
Identify the parts of a typical leaf; Describe the internal structure and function of a leaf;. In this (c) light micrograph cross-section of an A. lyrata leaf, the guard cell pair is visible along with the large, sub-stomatal air space in the leaf. (credit: modification of work by Robert R. Wise; part c scale-bar data from Matt Russell).

Labeled Diagram Of A Leaf hubpages
The leaves of dicotyledonous plants are arranged in a horizontal position, i.e., at a right angle to the rays of the sun so that they receive more light on the upper surface than the lower surface. The leaves with such an arrangement are known as dorsiventral or bifacial leaves.